Aperture REST API calls as Datasets within Aperture

Data is available from Aperture via the REST API that is not available in Aperture. Full details of Spaces, User Groups, Users, Jobs, Datasets etc.
We would like to use Aperture to manage Aperture.
For example: An automated workflow which checks for long running jobs and notifies us of issues; a regular review of user activity which allows us to remove access from inactive users, producing data quality stats which are already enriched with Space metadata and which automatically update when a new Space is created.
We can see that there is already a JDBC driver which ought to be able to do this (Autonomous REST 6.0) but the configuration is highly complex. Ideally we would have a config file that sets up all GET calls from the API and makes them available as datasets which we can then use in our Data Quality Management space (and activities).
Has anyone configured the Autonomous REST driver to access the Aperture API ?
If not, could Experian provide a documented example setup including a config file we can complete with the details of our own server ?
Best Answer
-
Hi @Dom Gittins , really glad that you ask this question because I think there's a lot of potential here for interesting solutions that use the native Autonomous REST JDBC driver with Data Studio's REST API to create interesting and useful management / admin dashboards.
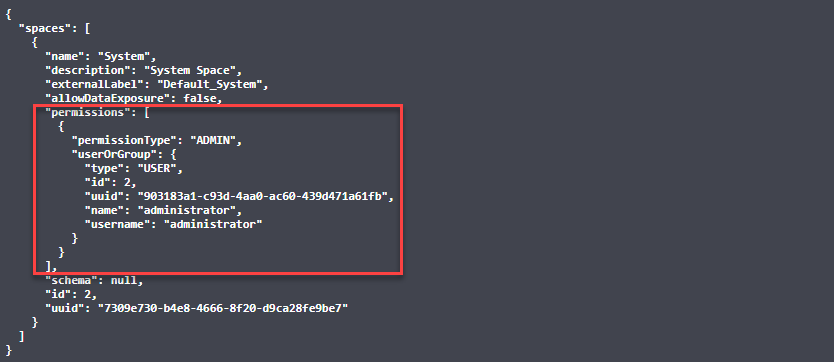
It can be a bit fiddly to set up the AutoREST connector so that the REST API's JSON responses are correctly parsed to tables - particularly when the response contains a nested array of values. In these cases, the driver normalizes the nested array to a child table which can be joined via a key from the parent table. An example of this is the /spaces endpoint, which returns an array of users and groups that have access to each space:
I'll show later how this is handled by Data Studio - to start with, here's how I've set up the External System to connect to Data Studio's API:
- Create an API key - Both the API key and the REST API calls you make are environment-specific, so if you have multiple environments you'll need to manage them with separate keys and tables. The API key only needs Read access to the endpoint you are interested in.
Create a new External System using the Autonomous REST connector. We're going to use a .rest file to list the endpoints and the schemas for the resulting data. The settings you need for this are:
- Servername = The hostname of the Data Studio server. So if you API documentation is at https://local.datastudio/api/docs/index.html, the servername setting should be "https://local.datastudio"
- Rest config file: This will be the location on disk (on the Data Studio server) where we'll drop the attached .rest file
- Authentication = None (the auth is handled via the API call header rather than the driver auth
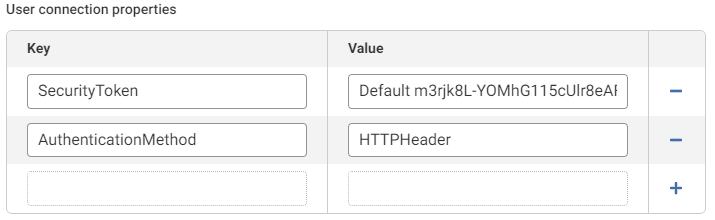
Then create two user connection properties:
- SecurityToken = "<environment_label><space><API_Key>". This is the same way you would authenticate with the REST API directly
- AuthenticationMethod = HTTPHeader
3 . You'll need to create a Credential for the External System to use, but this will just be a dummy value because the External System itself hlds the auth credentials
4 . Now drop the attached .rest file into the location you defined in the External System's "REST config file" setting. remove the ".txt" extension that I had to add to allow the file to be uploaded.
This .rest file defines the endpoints that allow you to load:
- Event information (/events)
- User session information (/sessions)
- Info on all Spaces - List Spaces (/spaces)
- Job execution information (/jobs)
- Dataset information - List Datasets (/datasets)
- Updated Nov 2024 to include ObjectTags
- Upaated Nov 2024 to include new properties "enableDropZone", "publishOData", "batchSettings", "batchLimit", "allowBatchDeletion" and "allowAutoRefresh".
- ExportableObjects - List exportable objects in a space, using space id 6 as an example (/exportableobjects/6) * added Nov 2023
- Metrics (/metrics) * added Nov 2023
- Functions - List all functions (/functions) * added Nov 2024
- Views - List all views (/views) * added Nov 2024
- External Systems - List all External Systems (/externalsystems) * added Nov 2024
- Credentials - List all credentials for an External System, using system id 5 as an example (/externalsystems/5/credentials) * added Nov 2024
To test the connection, go to Datasets -> Add Dataset and select the External System you have created. You should see the following list of tables generated by the .rest file's schema and available to load:
Here we also see how nested arrays are normalized. The SPACES table has a child SPACES_PERMISSIONS table. The "ID" column in the SPACES table is the join key into SPACES_PERMISSIONS (where the column is called SPACES_ID). By joining these in a workflow, you'll get a view of all spaces and associated user & group permissions:
JOBS also has a child table (key is the executionID), and DATASETS has a more complicated structure because a Dataset can include more than one Table, and a Table can have multiple batches of data, as well as multiple columns and tags.
6
Answers
-
Some ideas for things to could do with this Data Studio metadata.
- Monitoring and email alerting on unusual login activity via the Events table
- Create dashboards showing all users' admin access, as a way of checking that permissions aren't too broad
- Analysis of Job execution times - checking and alerting if certain jobs are running in parallel.
- Finding where your large Datasets are (based on number of rows & columns) that may be hogging disk space
- Add in the Metrics operation endpoint and create a dashboard to monitor things like CPU usage, or page responsiveness
2 -
Great question @Dom Gittins (and nice response @Henry Simms).
I've just given this a go myself and it worked a treat.
Just as an FYI for anyone else giving this a go I found that the file you attached downloaded as a .txt (so it needed renaming to get rid of this extension).
I'm currently using this approach to help @Sharat Kutty generate a list of all datasets within a 'master data' space and expose this as a list for other users to see what 'Enterprise Data' is available (i.e. the catalogue of data that they can request access to, via a shared View). What's nice about this is that you can pull through all of the metadata e.g. source type, column name, datatype, dataset rowcount, summary/description fields and more. Nice for encouraging consistent use (in line with any defined best practises) of the software
1 -
A couple of people have hit a problem where, after setting up the REST API connection, loaded tables from the new AutoREST system have 0 rows. That's accompanied by an error in the log file along the lines of:
java.sql.SQLException: [ApertureDataStudio][AutoREST JDBC Driver][AutoREST]I/O Error com.experian.aperturedatastudio.autorest.util.aj: SSL handshake failed: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested targetThis is a site certificate error, and essentially indicates that Data Studio doesn't trust the API calls it's making to itself.
With this set-up, Data Studio is acting like a client to its own API, but doesn't have its own certificate in its truststore - only it's key store. That's quite likely to happen if you're using a certificate from a private CA.
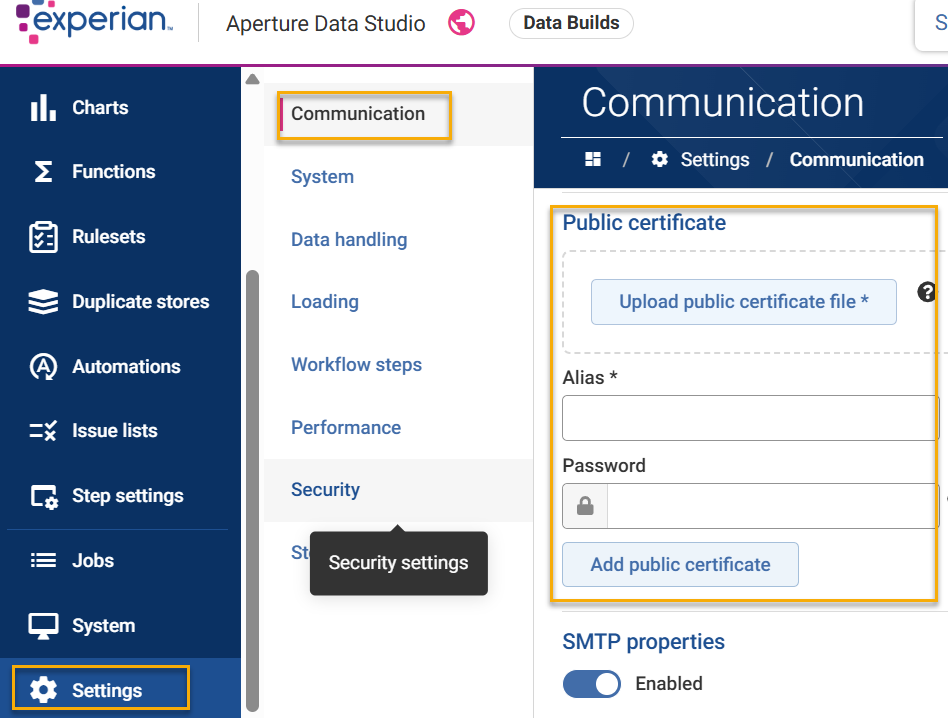
The fix is to add the public certificate from Data Studio into the cacerts truststore it uses. Steps:
- Get the public certificate. You can grab this from the browser and download (export) to a .cer file or similar
- Add this new public certificate to Data Studio's truststore via the Setting > Communication > Public Certificate dialog. You will not typically have a password for the public cert, and the alias can be whatever you want (I use "aperture_cert")
Note on older versions
If your version of Aperture does not have a Public Certificate section in Settings and you cannot carry out the steps listed above, you may need to apply the public certificate using the Java keytool instead. Steps to do this:
Run the following command from the command line to import them into the Aperture Data Studio truststore:
"<JRE path>\bin\keytool" -import -trustcacerts -alias <alias> -file "<Your own Certificate>.crt" -keystore "<database path>\certificates\cacerts"Where:
- <JRE path> is C:\Program Files\Experian\Aperture Data Studio 2.9.6\java64\jre, where you'll need to modify for your own version number and drive letter, if not C:\
- <alias> is anything you want
- <Your own Certificate> the full path to your public key file
- <database path> = D:\aperturedatastudio, again you may be using a different drive letter
1 -
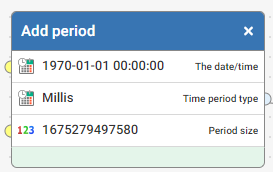
Love this! For anyone downloading Jobs API, the start and end times are epoch time, which is "the number of seconds that have elapsed since January 1, 1970" whilst fairly standard for API, not useful for a human, so this Function can be used to transform:
2 -
I've also just added a new reusable function to the Community Function library for this :) https://community.experianaperture.io/discussion/971/convert-epoch-date-time-to-standard-date-time/
2 -
Update that I discovered recently: If you don't want to expose the API key used by the External System in the Data Studio UI, you can add it to the .rest config file instead. So rather than:
you can add the following lines to the top of your .rest file:
"#options": {
"authenticationmethod": {
"choices": "HTTPHeader",
"default": "HTTPHeader"
}
},and then for each table add:
"#headers": {
"Authorization": "Default SzSkkIW0t9VJMLpEqGd..<etc>",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},The file should look something like this:
1 -
@Henry Simms could we use this process to connect with an external system such as Zendesk? the idea is to download the data from Zendesk and upload it within a Aperture Space.
Many thanks in advance for your support.
1 -
Hi @Marco_13112001 - Yes, it should certainly be possible to use the Autonomous REST connector to pull data from the Zendesk REST API. To get started I would recommend:
- Using Postman or a similar tool, ensure that you can use the API directly to do the things you need, and have the correct auth credentials etc
- Run the driver's Configuration Manager from the commandline to begin configuring the connection info you'll need when using the AutoREST driver in Data Studio
- Run
"C:\Program Files\Experian\Aperture Data Studio 2.11.3\java64\bin\java.exe" -jar DSautorest.jar. (you will likely need to update your path to the java.exe used by your version of Data Studio) - By default, running the jar will pop up the "
Configuration Manager" (jdbc.html) page for the driver. To create the custom model (mappings, auth etc) for your API using the "Composer"(arc.html) page to generate a .rest file, as well as the connection string.
- Run
- Only when you have access to the normalised tables you need in the AutoREST composer, move the configuration to Aperture Data Studio
1 -
@Henry Simms Many thanks for your help. I'm using Postman as suggested to develop and test the API (I need to add that I'm still learning about the whole process), however even tough it is returning a 200 response it also brings an warning saying that it is "unable to find local certificate".
The post Request has the following structure - {{baseurl}}//api/v2/datasets/{space_id}/create?token={Aperture API key}. The Aperture key was setup to enable the creation of a dataset.
Am I using the wrong construct or it is an authorisation issue?
Many thanks thanks in advance.
1 -
Hi @Marco_13112001 , looks like there's a few things going on here.
- I can see it looks like you're looking at the Data Studio REST API. You won't need this to bring data from your ZenDesk API into Data Studio, because once you've got the External System set up (connected to Zendesk, with the driver's .rest file configured to normalise the responses you need into tables), you'll just be able to bring in the data like you do with any other Dataset, via the UI. You'll then be able to set up auto-refresh, also as with any other External System source dataset:
- If you do want to use the Data Studio REST API, there's a few changes to make to the way you're calling it in Postman:
- Move the authorization to the Header, and make sure you include the environment label ("Default" is the default) before the API key:
- If your Data Studio instance uses an SSL certificate from a private CA, or uses a self-signed certificate, you may need to add your certificate to Postman.
- Move the authorization to the Header, and make sure you include the environment label ("Default" is the default) before the API key:
0 - I can see it looks like you're looking at the Data Studio REST API. You won't need this to bring data from your ZenDesk API into Data Studio, because once you've got the External System set up (connected to Zendesk, with the driver's .rest file configured to normalise the responses you need into tables), you'll just be able to bring in the data like you do with any other Dataset, via the UI. You'll then be able to set up auto-refresh, also as with any other External System source dataset:
-
We recently needed to load data from the Exportable Objects endpoint of the Aperture API, so we could analyse dependencies between objects in bulk.
This is a per-space call (the space id is passed in the call), and the below snippet shows what you would need to add to your .rest file to bring back exportable objects from Space 6:
"exportableobjectsspace6": {
"#path": [
"/api/1/exportableobjects/6 /objectLists"
],
"objectType": "VarChar(64),#key",
"objects[]": {
"id": "Integer",
"name": "VarChar(76)",
"summary": "VarChar(241)",
"status": "VarChar(13)",
"dependsOn<exportableobjectsspace6_dependsOn>[]": {
"objectType": "VarChar(64)",
"id": "Integer",
"name": "VarChar(64)"
},
"forcedDependencies<exportableobjectsspace6_forcedDependencies>[]": {
"objectType": "VarChar(21)",
"id": "Integer",
"name": "VarChar(40)"
}
}
}This returns 3 related tables:
The first table contains the objects in the space, the second and third tables can be joined on (by OBJECTTYPE and POSITION) to view dependencies and forced dependencies
1 -
@Henry Simms I have used the attached .RESt file above and its working for me. Many Thanks for that. But it does not have all the available APIs. I was looking for the below ones as well, to check the Performance of our servers
I tried to get the through progress DataDirect using the Rest you shared as the existing model, but getting some Auth issue there.
0 -
Hi @Mahulima , I've updated the
datastudio_api.restfile in my original post to include tables for:- metrics. This will generate a single 486-column table containing all available metrics from the Aperture API:
- metrics/disc.metric. This specifically extracts the disk metric information from the Aperture API, and maps as multiple relational tables which would need to be joined:
Different metric names (call
metrics/listfor the list) will have different mappings.0 -
@Henry Simms Thank you so much! I tried and its working perfectly :)
0 -
I am facing one issue with Sessions API. When I am getting the response of the session it is showing me the start date as 28th Nov for me and for some regular active users and end date is null. I thought when we log off from the Aperture the session will be ended, but its not happening. Idea was to get active users for past 24 hrs. which I am not getting with Users API as well, as there it is only showing Last login as a date not as timestamp. But there getting the correct Information. Can you please help here. @Henry Simms
0 -
Hi @Mahulima - I can see the same behaviour, but can confirm that the problem isn't with the API, as you also see null enddate values in the repository database itself. I'll try to find out more about why some
sessionrecords do not store end dates1 -
Hi @Henry Simms , Is there a way we can get the details of the View as well, Currently from the attached rest file we are getting the dataset details but it only contains datasets, view details are missing
0 -
HI @Mahulima , the problem really is that the REST API doesn't provide much information about Views at the moment. While for Datasets, you can make a call to get lots of information about all Datasets in a space (e.g. source, refresh data, row count), for Views you can only really get sharing information for a specific View (based on an ID), or carry out operations for automatically sharing or including views.
If you're looking to list Views in a Space and gather metadata on those views, I think a new REST API endpoint would be needed. I would suggest putting an idea on the Ideas Board
0 -
@Henry Simms Thanks for your prompt response. I am trying to get the view information along with which all spaces the view has been shared and also when the last time the view has refreshed.
0